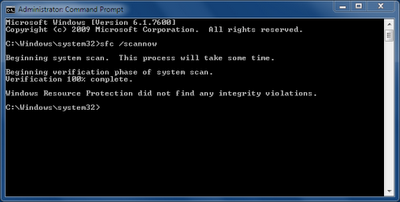
First you will need to start a permission-elevated command-line prompt. Typecommand into the Desktop Search box and then right-click on the Command Prompt menu entry and select the Run as Administrator item (Figure A).
Figure A
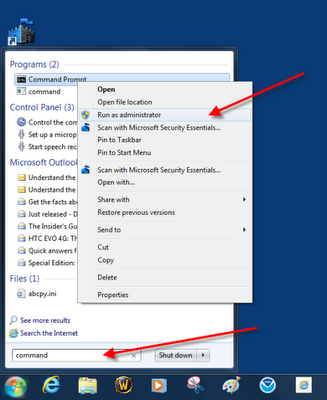
After accepting the elevated permissions, at the prompt type this command:
sfc /scannow
Now the system will verify the system
files and repair any corrupted files (Figure B).
Figure B
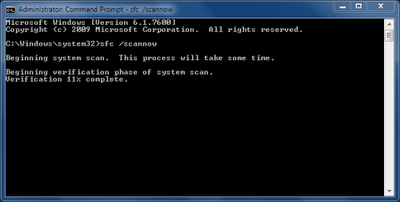
My test system had no errors (Figure C); however if it did, this scan would have repaired any corrupted files, but without forcing a system reboot.
Figure C